all about rfid
December 19, 2025
all about rfid proposal! all about rfid official support.GOV,all about rfid active!
# All About RFID: A Comprehensive Guide to Radio-Frequency Identification
## What Is RFID Technology?
**All about RFID** begins with understanding its fundamental principles. RFID, or Radio-Frequency Identification, is a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. These tags contain electronically stored information, which can be read from several meters away without requiring a direct line of sight. Unlike barcodes, RFID tags don't need to be within the view of the reader, making the process faster and more efficient.
From my personal experience working in logistics, implementing RFID systems transformed our inventory management. We reduced manual scanning errors by over 70% and cut inventory counting time from days to hours. The ability to read multiple tags simultaneously was particularly revolutionary for our operations.
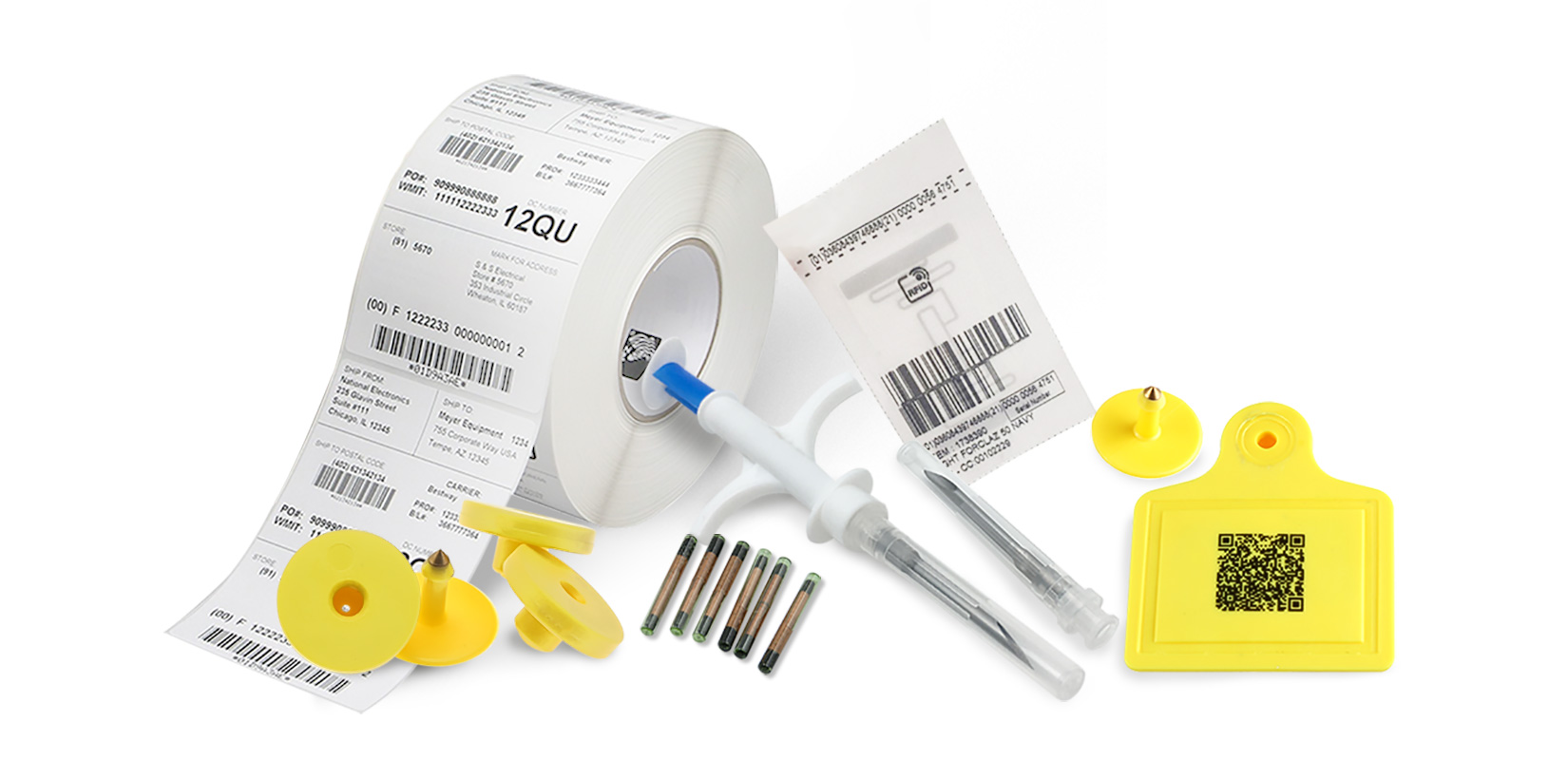 ## How RFID Technology Works
### Basic Components of RFID Systems
## How RFID Technology Works
### Basic Components of RFID Systems
 Every RFID system consists of three primary components:
1. **RFID Tags**: These contain microchips and antennas that store and transmit data
2. **RFID Readers**: Devices that send and receive radio signals to communicate with tags
3. **Antenna**: Facilitates communication between tags and readers
4. **Software System**: Processes and manages the collected data
My technical background in electrical engineering gave me a unique perspective on RFID implementation. I discovered that my natural aptitude for understanding radio wave propagation helped me optimize RFID system layouts for maximum efficiency in challenging environments like metal-rich warehouses.
## Types of RFID Systems
### Frequency Classifications
RFID systems operate at different frequencies, each with distinct characteristics:
**Low Frequency (LF) RFID:**
- Frequency range: 30 kHz to 300 kHz
Every RFID system consists of three primary components:
1. **RFID Tags**: These contain microchips and antennas that store and transmit data
2. **RFID Readers**: Devices that send and receive radio signals to communicate with tags
3. **Antenna**: Facilitates communication between tags and readers
4. **Software System**: Processes and manages the collected data
My technical background in electrical engineering gave me a unique perspective on RFID implementation. I discovered that my natural aptitude for understanding radio wave propagation helped me optimize RFID system layouts for maximum efficiency in challenging environments like metal-rich warehouses.
## Types of RFID Systems
### Frequency Classifications
RFID systems operate at different frequencies, each with distinct characteristics:
**Low Frequency (LF) RFID:**
- Frequency range: 30 kHz to 300 kHz
 - Typical reading range: Up to 10 cm
- Common applications: Animal tracking, access control, car immobilizers
**High Frequency (HF) RFID:**
- Frequency range: 3 MHz to 30 MHz
- Typical reading range: Up to 10 cm
- Common applications: Animal tracking, access control, car immobilizers
**High Frequency (HF) RFID:**
- Frequency range: 3 MHz to 30 MHz
 - Typical reading range: 10 cm to 1 meter
- Common applications: Smart cards, library books, payment systems
**Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) RFID:**
- Frequency range: 300 MHz to 3 GHz
- Typical reading range: Up to 12 meters
- Common applications: Supply chain management, retail inventory, logistics
**Microwave RFID:**
- Typical reading range: 10 cm to 1 meter
- Common applications: Smart cards, library books, payment systems
**Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) RFID:**
- Frequency range: 300 MHz to 3 GHz
- Typical reading range: Up to 12 meters
- Common applications: Supply chain management, retail inventory, logistics
**Microwave RFID:**
 - Frequency range: 2.45 GHz to 5.8 GHz
- Typical reading range: Over 30 meters
- Common applications: Vehicle tracking, automated toll collection
## Technical Specifications of RFID Products
### TIANJUN RFID Reader Technical Parameter
- Frequency range: 2.45 GHz to 5.8 GHz
- Typical reading range: Over 30 meters
- Common applications: Vehicle tracking, automated toll collection
## Technical Specifications of RFID Products
### TIANJUN RFID Reader Technical Parameter
The Use of RFID for Human Identity Verification
 ## How RFID Technology Works
### Basic Components of RFID Systems
## How RFID Technology Works
### Basic Components of RFID Systems
 Every RFID system consists of three primary components:
1. **RFID Tags**: These contain microchips and antennas that store and transmit data
2. **RFID Readers**: Devices that send and receive radio signals to communicate with tags
3. **Antenna**: Facilitates communication between tags and readers
4. **Software System**: Processes and manages the collected data
My technical background in electrical engineering gave me a unique perspective on RFID implementation. I discovered that my natural aptitude for understanding radio wave propagation helped me optimize RFID system layouts for maximum efficiency in challenging environments like metal-rich warehouses.
## Types of RFID Systems
### Frequency Classifications
RFID systems operate at different frequencies, each with distinct characteristics:
**Low Frequency (LF) RFID:**
- Frequency range: 30 kHz to 300 kHz
Every RFID system consists of three primary components:
1. **RFID Tags**: These contain microchips and antennas that store and transmit data
2. **RFID Readers**: Devices that send and receive radio signals to communicate with tags
3. **Antenna**: Facilitates communication between tags and readers
4. **Software System**: Processes and manages the collected data
My technical background in electrical engineering gave me a unique perspective on RFID implementation. I discovered that my natural aptitude for understanding radio wave propagation helped me optimize RFID system layouts for maximum efficiency in challenging environments like metal-rich warehouses.
## Types of RFID Systems
### Frequency Classifications
RFID systems operate at different frequencies, each with distinct characteristics:
**Low Frequency (LF) RFID:**
- Frequency range: 30 kHz to 300 kHz
 - Typical reading range: Up to 10 cm
- Common applications: Animal tracking, access control, car immobilizers
**High Frequency (HF) RFID:**
- Frequency range: 3 MHz to 30 MHz
- Typical reading range: Up to 10 cm
- Common applications: Animal tracking, access control, car immobilizers
**High Frequency (HF) RFID:**
- Frequency range: 3 MHz to 30 MHz
 - Typical reading range: 10 cm to 1 meter
- Common applications: Smart cards, library books, payment systems
**Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) RFID:**
- Frequency range: 300 MHz to 3 GHz
- Typical reading range: Up to 12 meters
- Common applications: Supply chain management, retail inventory, logistics
**Microwave RFID:**
- Typical reading range: 10 cm to 1 meter
- Common applications: Smart cards, library books, payment systems
**Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) RFID:**
- Frequency range: 300 MHz to 3 GHz
- Typical reading range: Up to 12 meters
- Common applications: Supply chain management, retail inventory, logistics
**Microwave RFID:**
 - Frequency range: 2.45 GHz to 5.8 GHz
- Typical reading range: Over 30 meters
- Common applications: Vehicle tracking, automated toll collection
## Technical Specifications of RFID Products
### TIANJUN RFID Reader Technical Parameter
- Frequency range: 2.45 GHz to 5.8 GHz
- Typical reading range: Over 30 meters
- Common applications: Vehicle tracking, automated toll collection
## Technical Specifications of RFID Products
### TIANJUN RFID Reader Technical ParameterPhone: +86 19925232774
Hours: Mon-Fri 9:00AM - 6:30PM